TA的每日心情 | 无聊
5 天前 |
|---|
签到天数: 1050 天 连续签到: 1 天 [LV.10]测试总司令
|
图像处理已经成为我们日常生活中不可或缺的一部分,涉及到社交媒体和医学成像等各个领域。通过数码相机或卫星照片和医学扫描等其他来源获得的图像可能需要预处理以消除或增强噪声。频域滤波是一种可行的解决方案,它可以在增强图像锐化的同时消除噪声。
快速傅里叶变换(FFT)是一种将图像从空间域变换到频率域的数学技术,是图像处理中进行频率变换的关键工具。通过利用图像的频域表示,我们可以根据图像的频率内容有效地分析图像,从而简化滤波程序的应用以消除噪声。本文将讨论图像从FFT到逆FFT的频率变换所涉及的各个阶段,并结合FFT位移和逆FFT位移的使用。
本文使用了三个Python库,即openCV、Numpy和Matplotlib。
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('sample.png',0) # Using 0 to read image in grayscale mode
plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray') #cmap is used to specify imshow that the image is in greyscale
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) # remove tick marks
plt.show()
1、快速傅里叶变换(FFT)
快速傅里叶变换(FFT)是一种广泛应用的数学技术,它允许图像从空间域转换到频率域,是频率变换的基本组成部分。利用FFT分析,可以得到图像的周期性,并将其划分为不同的频率分量,生成图像频谱,显示每个图像各自频率成分的振幅和相位。
f = np.fft.fft2(img) #the image 'img' is passed to np.fft.fft2() to compute its 2D Discrete Fourier transform f
mag = 20*np.log(np.abs(f))
plt.imshow(mag, cmap = 'gray') #cmap='gray' parameter to indicate that the image should be displayed in grayscale.
plt.title('Magnitude Spectrum')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
上面代码使用np.abs()计算傅里叶变换f的幅度,np.log()转换为对数刻度,然后乘以20得到以分贝为单位的幅度。这样做是为了使幅度谱更容易可视化和解释。
2、FFT位移
为了使滤波算法应用于图像,利用FFT移位将图像的零频率分量被移动到频谱的中心
fshift = np.fft.fftshift(f)
mag = 20*np.log(np.abs(fshift))
plt.imshow(mag, cmap = 'gray')
plt.title('Centered Spectrum'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
3、过滤
频率变换的的一个目的是使用各种滤波算法来降低噪声和提高图像质量。两种最常用的图像锐化滤波器是Ideal high-pass filter 和Gaussian high-pass filter。这些滤波器都是使用的通过快速傅里叶变换(FFT)方法获得的图像的频域表示。
Ideal high-pass filter(理想滤波器) 是一种无限长的、具有无限频带宽和理想通带和阻带响应的滤波器。其通带内所有频率的信号都被完全传递,而阻带内所有频率的信号则完全被抑制。
在频域上,理想滤波器的幅频响应为:
· 在通带内,幅频响应为 1
· 在阻带内,幅频响应为 0
在时域上,理想滤波器的冲激响应为:
· 在通带内,冲激响应为一个无限长的单位冲激函数序列
· 在阻带内,冲激响应为零
由于理想滤波器在频域上具有无限带宽,因此它无法在实际应用中实现。实际中使用的数字滤波器通常是基于理想滤波器的逼近,所以才被成为只是一个Ideal。
高斯高通滤波器(Gaussian high-pass filter)是一种在数字图像处理中常用的滤波器。它的作用是在图像中保留高频细节信息,并抑制低频信号。该滤波器基于高斯函数,具有光滑的频率响应,可以适应各种图像细节。
高斯高通滤波器的频率响应可以表示为:
H(u,v) = 1 - L(u,v)
其中,L(u,v)是一个低通滤波器,它可以用高斯函数表示。通过将低通滤波器的响应从1中减去,可以得到一个高通滤波器的响应。在实际中,通常使用不同的参数设置来调整高斯函数,以达到不同的滤波效果。
圆形掩膜(disk-shaped images)是用于定义在图像中进行傅里叶变换时要保留或抑制的频率分量。在这种情况下,理想滤波器通常是指理想的低通或高通滤波器,可以在频域上选择保留或抑制特定频率范围内的信号。将这个理想滤波器应用于图像的傅里叶变换后,再进行逆变换,可以得到经过滤波器处理后的图像。
具体的细节我们就不介绍了,直接来看代码:
下面函数是生成理想高通和低通滤波器的圆形掩膜
import math
def distance(point1,point2):
return math.sqrt((point1[0]-point2[0])**2 + (point1[1]-point2[1])**2)
def idealFilterLP(D0,imgShape):
base = np.zeros(imgShape[:2])
rows, cols = imgShape[:2]
center = (rows/2,cols/2)
for x in range(cols):
for y in range(rows):
if distance((y,x),center) < D0:
base[y,x] = 1
return base
def idealFilterHP(D0,imgShape):
base = np.ones(imgShape[:2])
rows, cols = imgShape[:2]
center = (rows/2,cols/2)
for x in range(cols):
for y in range(rows):
if distance((y,x),center) < D0:
base[y,x] = 0
return base
下面函数生成一个高斯高、低通滤波器与所需的圆形掩膜
import math
def distance(point1,point2):
return math.sqrt((point1[0]-point2[0])**2 + (point1[1]-point2[1])**2)
def gaussianLP(D0,imgShape):
base = np.zeros(imgShape[:2])
rows, cols = imgShape[:2]
center = (rows/2,cols/2)
for x in range(cols):
for y in range(rows):
base[y,x] = math.exp(((-distance((y,x),center)**2)/(2*(D0**2))))
return base
def gaussianHP(D0,imgShape):
base = np.zeros(imgShape[:2])
rows, cols = imgShape[:2]
center = (rows/2,cols/2)
for x in range(cols):
for y in range(rows):
base[y,x] = 1 - math.exp(((-distance((y,x),center)**2)/(2*(D0**2))))
return base
过滤示例
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 2) # create a 2x2 grid of subplots
fig.suptitle('Filters') # set the title for the entire figure
# plot the first image in the top-left subplot
im1 = ax[0, 0].imshow(np.abs(idealFilterLP(50, img.shape)), cmap='gray')
ax[0, 0].set_title('Low Pass Filter of Diameter 50 px')
ax[0, 0].set_xticks([])
ax[0, 0].set_yticks([])
# plot the second image in the top-right subplot
im2 = ax[0, 1].imshow(np.abs(idealFilterHP(50, img.shape)), cmap='gray')
ax[0, 1].set_title('High Pass Filter of Diameter 50 px')
ax[0, 1].set_xticks([])
ax[0, 1].set_yticks([])
# plot the third image in the bottom-left subplot
im3 = ax[1, 0].imshow(np.abs(gaussianLP(50 ,img.shape)), cmap='gray')
ax[1, 0].set_title('Gaussian Filter of Diameter 50 px')
ax[1, 0].set_xticks([])
ax[1, 0].set_yticks([])
# plot the fourth image in the bottom-right subplot
im4 = ax[1, 1].imshow(np.abs(gaussianHP(50 ,img.shape)), cmap='gray')
ax[1, 1].set_title('Gaussian Filter of Diameter 50 px')
ax[1, 1].set_xticks([])
ax[1, 1].set_yticks([])
# adjust the spacing between subplots
fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.5, hspace=0.5)
# save the figure to a file
fig.savefig('filters.png', bbox_inches='tight')

相乘过滤器和移位的图像得到过滤图像
为了获得具有所需频率响应的最终滤波图像,关键是在频域中对移位后的图像与滤波器进行逐点乘法。
这个过程将两个图像元素的对应像素相乘。例如,当应用低通滤波器时,我们将对移位的傅里叶变换图像与低通滤波器逐点相乘。
此操作抑制高频并保留低频,对于高通滤波器反之亦然。这个乘法过程对于去除不需要的频率和增强所需的频率是必不可少的,从而产生更清晰和更清晰的图像。
它使我们能够获得期望的频率响应,并在频域获得最终滤波图像。
4、乘法滤波器(Multiplying Filter)和平移后的图像(Shifted Image)
乘法滤波器是一种以像素值为权重的滤波器,它通过将滤波器的权重与图像的像素值相乘,来获得滤波后的像素值。具体地,假设乘法滤波器的权重为h(i,j),图像的像素值为f(m,n),那么滤波后的像素值g(x,y)可以表示为:
g(x,y) = ∑∑ f(m,n)h(x-m,y-n)
其中,∑∑表示对所有的(m,n)进行求和。
平移后的图像是指将图像进行平移操作后的结果。平移操作通常是指将图像的像素沿着x轴和y轴方向进行平移。平移后的图像与原始图像具有相同的大小和分辨率,但它们的像素位置发生了变化。在滤波操作中,平移后的图像可以用于与滤波器进行卷积运算,以实现滤波操作。
此操作抑制高频并保留低频,对于高通滤波器反之亦然。这个乘法过程对于去除不需要的频率和增强所需的频率是必不可少的,从而产生更清晰和更清晰的图像。
它使我们能够获得期望的频率响应,并在频域获得最终滤波图像。
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
im = ax.imshow(np.log(1+np.abs(fftshifted_image * idealFilterLP(50,img.shape))), cmap='gray')
ax.set_title('Filtered Image in Frequency Domain')
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
fig.savefig('filtered image in freq domain.png', bbox_inches='tight')
在可视化傅里叶频谱时,使用np.log(1+np.abs(x))和20*np.log(np.abs(x))之间的选择是个人喜好的问题,可以取决于具体的应用程序。
一般情况下会使用Np.log (1+np.abs(x)),因为它通过压缩数据的动态范围来帮助更清晰地可视化频谱。这是通过取数据绝对值的对数来实现的,并加上1以避免取零的对数。
而20*np.log(np.abs(x))将数据按20倍缩放,并对数据的绝对值取对数,这可以更容易地看到不同频率之间较小的幅度差异。但是它不会像np.log(1+np.abs(x))那样压缩数据的动态范围。
这两种方法都有各自的优点和缺点,最终取决于具体的应用程序和个人偏好。
5、逆FFT位移
在频域滤波后,我们需要将图像移回原始位置,然后应用逆FFT。为了实现这一点,需要使用逆FFT移位,它反转了前面执行的移位过程。
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
im = ax.imshow(np.log(1+np.abs(np.fft.ifftshift(fftshifted_image * idealFilterLP(50,img.shape)))), cmap='gray')
ax.set_title('Filtered Image inverse fft shifted')
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
fig.savefig('filtered image inverse fft shifted.png', bbox_inches='tight')
6、快速傅里叶逆变换(IFFT)
快速傅里叶逆变换(IFFT)是图像频率变换的最后一步。它用于将图像从频域传输回空间域。这一步的结果是在空间域中与原始图像相比,图像减少了噪声并提高了清晰度。
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
im = ax.imshow(np.log(1+np.abs(np.fft.ifft2(np.fft.ifftshift(fftshifted_image * idealFilterLP(50,img.shape))))), cmap='gray')
ax.set_title('Final Filtered Image In Spatial Domain')
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
fig.savefig('final filtered image.png', bbox_inches='tight')
总结
我们再把所有的操作串在一起显示,函数绘制所有图像。
def Freq_Trans(image, filter_used):
img_in_freq_domain = np.fft.fft2(image)
# Shift the zero-frequency component to the center of the frequency spectrum
centered = np.fft.fftshift(img_in_freq_domain)
# Multiply the filter with the centered spectrum
filtered_image_in_freq_domain = centered * filter_used
# Shift the zero-frequency component back to the top-left corner of the frequency spectrum
inverse_fftshift_on_filtered_image = np.fft.ifftshift(filtered_image_in_freq_domain)
# Apply the inverse Fourier transform to obtain the final filtered image
final_filtered_image = np.fft.ifft2(inverse_fftshift_on_filtered_image)
return img_in_freq_domain,centered,filter_used,filtered_image_in_freq_domain,inverse_fftshift_on_filtered_image,final_filtered_image
使用高通、低通理想滤波器和高斯滤波器的直径分别为50、100和150像素,展示它们对增强图像清晰度的影响。
fig, axs = plt.subplots(12, 7, figsize=(30, 60))
filters = [(f, d) for f in [idealFilterLP, idealFilterHP, gaussianLP, gaussianHP] for d in [50, 100, 150]]
for row, (filter_name, filter_diameter) in enumerate(filters):
# Plot each filter output on a separate subplot
result = Freq_Trans(img, filter_name(filter_diameter, img.shape))
for col, title, img_array in zip(range(7),
["Original Image", "Spectrum", "Centered Spectrum", f"{filter_name.__name__} of Diameter {filter_diameter} px",
f"Centered Spectrum multiplied by {filter_name.__name__}", "Decentralize", "Processed Image"],
[img, np.log(1+np.abs(result[0])), np.log(1+np.abs(result[1])), np.abs(result[2]), np.log(1+np.abs(result[3])),
np.log(1+np.abs(result[4])), np.abs(result[5])]):
axs[row, col].imshow(img_array, cmap='gray')
axs[row, col].set_title(title)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('all_processess.png', bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
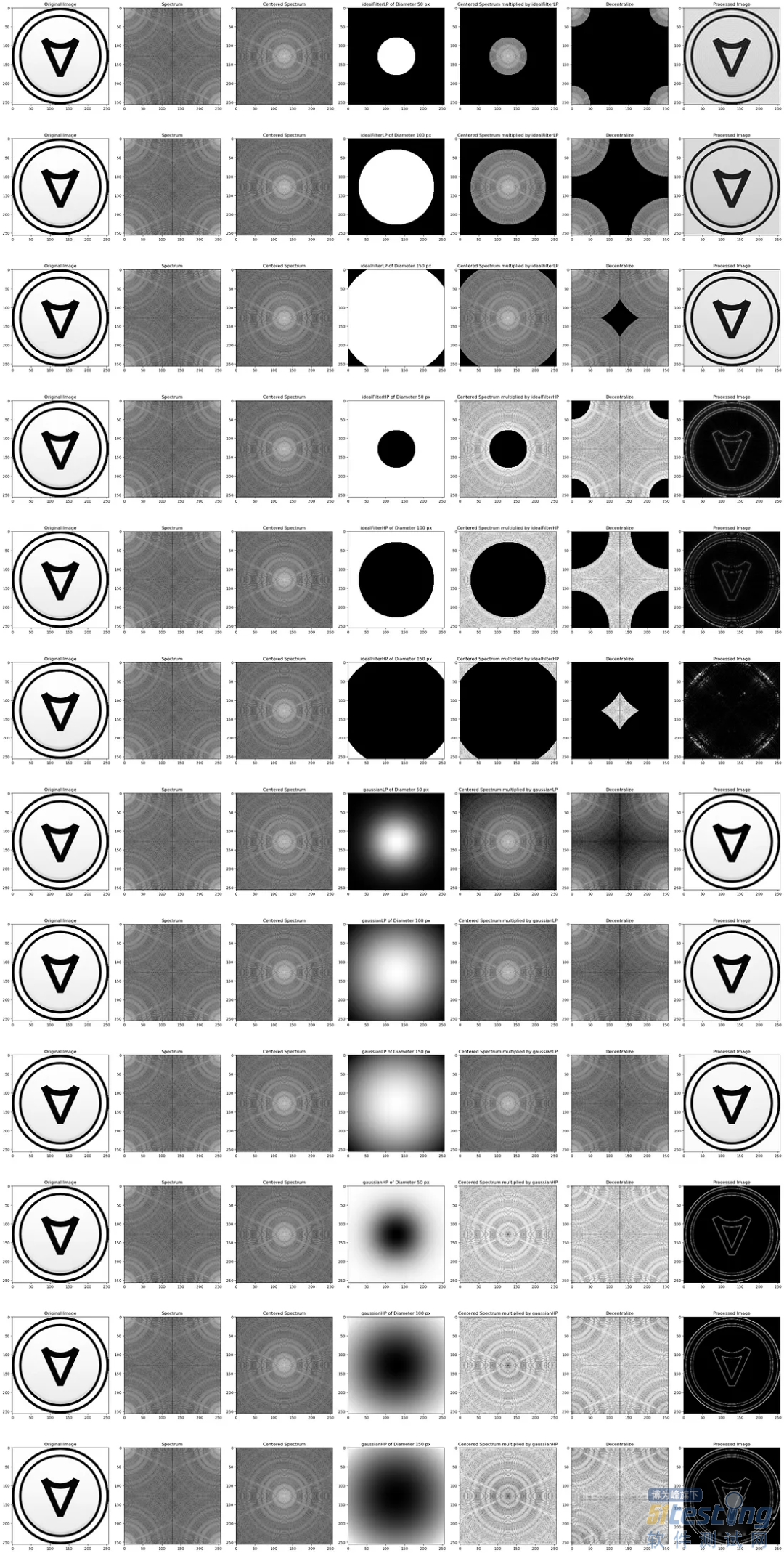
可以看到,当改变圆形掩膜的直径时,对图像清晰度的影响会有所不同。随着直径的增加,更多的频率被抑制,从而产生更平滑的图像和更少的细节。减小直径允许更多的频率通过,从而产生更清晰的图像和更多的细节。为了达到理想的效果,选择合适的直径是很重要的,因为使用太小的直径会导致过滤器不够有效,而使用太大的直径会导致丢失太多的细节。
一般来说,高斯滤波器由于其平滑性和鲁棒性,更常用于图像处理任务。在某些应用中,需要更尖锐的截止,理想滤波器可能更适合。
利用FFT修改图像频率是一种有效的降低噪声和提高图像锐度的方法。这包括使用FFT将图像转换到频域,使用适当的技术过滤噪声,并使用反FFT将修改后的图像转换回空间域。通过理解和实现这些技术,我们可以提高各种应用程序的图像质量。
|
|
 /1
/1 
 关于我们
关于我们